🔎 搜索 & 图论
- 备注:基于
Acwing的irai个人笔记记录
一、DFS
1.1 排列数字
- 模板题:842. 排列数字
- 示例代码:
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
const int N = 10;
// path : 路径 ; st : 状态数组(i 有没有被用过)
int path[N];
bool st[N];
int n; // n 在全局变量位置,dfs 函数内可以用到
void dfs(int u){
if(u == n){
//走到头了,那么可以输出 path
for(int i = 0; i < n; i ++ ) cout << path[i] << ' ';
cout << endl;
return;
}
for(int i = 1; i <= n; i ++ ){ // 数字范围是从 1 ~ n
if(!st[i]){
// 如果这个数没有用过的话
path[u] = i; // 注意位置是传入的参数 u , 数字是 i
st[i] = true; // 在进入递归之前 , 标记 i 被使用
dfs(u + 1); // 下一个位置
// 恢复现场
st[i] = false;
}
}
}
int main()
{
cin >> n;
dfs(0); // 从 path 的第 0 个位置开始 dfs
return 0;
}1.2 n - 皇后问题
分析问题:
n 皇后问题即是深搜 ( DFS ) 问题,与之前的排列数字相同,是在一定的约束条件下进行的
在排列数字中,约束由
if(!st[i])这句表明,即不能使用前面用过的数字,在那个代码里我们使用了
st[](state n.状态) 状态数组来标记数字的使用情况。那么在 n 皇后问题里要求的约束条件复杂一些:
即任意两个皇后都不能处于 同一行、同一列或同一斜线上 。
那么如何判断两个皇后是否在 同一行、同一列、同一斜线上 呢?这是解题的关键,
我们依然使用数组。具体为
row[], col[], dg[], udg[]。 (diagonaln. 对角线,斜线 )
if (!row[x] && !col[y] && !dg[x - y + n] && !udg[x + y])此代码为是否放皇后的判断语句。
row[x]和col[y]的意思很明显, 如果为false,即代表之前没有皇后下在了相同的 x 或 y 的行列上,本次就可以下皇后。不好理解的点是
dg[x - y + n]以及udia[x + y]请看下面的分析:
1). 对于判断是否在同一主对斜线(棋盘内与主对角线平行的斜线),我们使用
dg[]数组,可以任取一个棋盘位
(x,y), 并观察主斜线上该点与其它点位的规律:
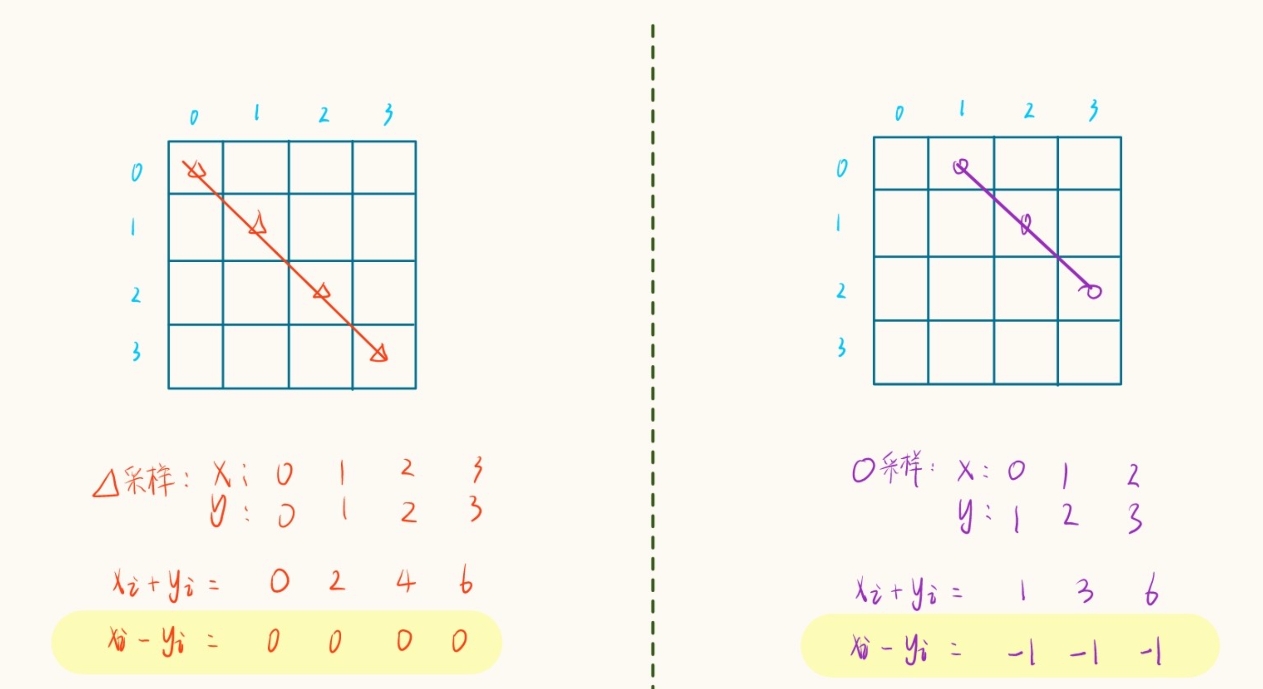
可以发现:主斜线上采样的多个点的 x、y 值的差是一样的,即说明多个点可通过减法映射到数组中
的同一位置,判断斜线上是否出现过一次皇后,即查看
dia[x - y]是否为false即可。但这样做减法时可能会得到一个负数,是没法直接映射到数组中的,因此主斜线上做判断时
统一加上一个常量保证非负,即
dia[x - y + n]。
2). 同理,对于判断是否在同一副斜线(棋盘内与副对角线平行的斜线),我们使用
udg[]数组,可以任取一个棋盘位
(x,y), 并观察副斜线上该点与其他点位的规律:
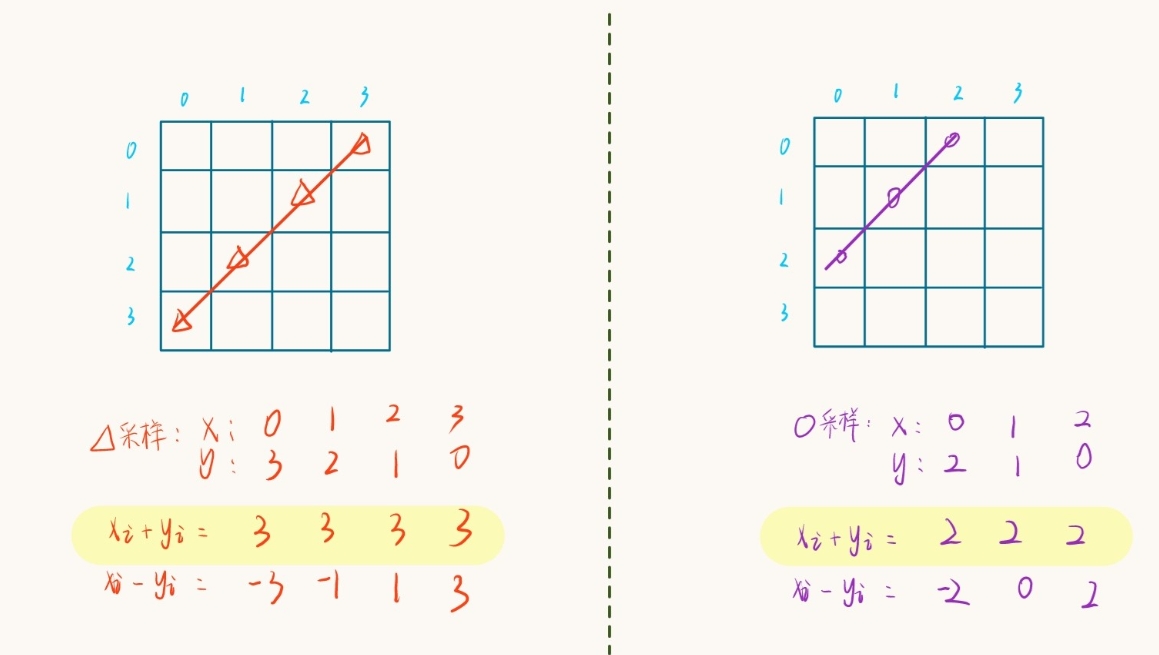
可以发现:主斜线上采样的多个点的 x、y 值的和是一样的,即说明多个点可通过加法映射到数组中
的同一位置,判断斜线上是否出现过一次皇后,即判断
udg[x + y]是否为false即可。
- 示例代码:
// 当前搜索顺序是从棋盘的左上角开始,自上而下,自左而右
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
const int N = 10;
int n;
// g[][] 存储棋盘
char g[N][N];
// 在这里 dg 是主斜线,udg 是副斜线
// 因为斜线的数量是 2n - 1 , 所以开到 N * 2 个
bool row[N],col[N], dg[N * 2], udg[N * 2];
void dfs(int x,int y, int s){
if(y == n) y = 0, x ++ ; // 向右到边界了,强制放到下一行第一个位置
if(x == n){
// 向下遍历到边界了
// 如果放的皇后数量 为 n 的话即找到了一组解
if(s == n){
for(int i = 0; i < n; i ++ ) cout << g[i] << endl;
cout << endl;
}
return;
}
// 当前格子不放皇后
dfs(x, y + 1, s);
// 当前格子放皇后
if(!row[x] && !col[y] && !dg[x - y + n] && !udg[x + y]){
g[x][y] = 'Q'; // 放皇后
row[x] = col[y] = dg[x - y + n] = udg[x + y] = true; // 标记
dfs(x, y + 1, s + 1);
// 恢复现场
row[x] = col[y] = dg[x - y + n] = udg[x + y] = false;
g[x][y] = '.';
}
}
int main()
{
// 接收 n
cin >> n;
// 初始化棋盘
for(int i = 0; i < n; i ++ )
for(int j = 0; j < n; j ++ )
g[i][j] = '.';
// 三个参数分别是开始搜索的行、列以及当前放下了多少个皇后
// 即从左上角开始搜索
dfs(0,0,0);
return 0;
}二、BFS
模板题:844. 走迷宫
示例代码:
#include <iostream>
#include <cstring>
#include <cstdio>
using namespace std;
typedef pair<int,int> PII; // pair 用来存储坐标
const int N = 110;
// g[][] 是 grid 用来存储输入的图
int g[N][N];
// d[][] 是 distance 用来存储每个点离原点的最短距离
int d[N][N];
// 用于 bfs 的队列
PII q[N * N];
// n * m 的二维数组
int n, m;
// 宽搜,返回的是终点的最短距离
int bfs(){
// 这里都初始化为 0 是因为一开始要加入起点,所以队列有一个元素
int hh = 0, tt = 0;
// 加入起点
q[0] = {0, 0};
// 起点距离为 0;
d[0][0] = 0;
// 方向 上右下左
int dx[4] = {-1,0,1,0}, dy[4] = {0,1,0,-1};
while(hh <= tt){
// 队列不空一直搜
// 取出队头
auto t = q[ hh ++ ];
// 扩展队头四个方向
for(int i = 0; i < 4; i ++ ){
// 下一个点的坐标
int x = t.first + dx[i], y = t.second + dy[i];
// 如果下一个点合法,那么扩展
if(x >= 0 && x < n && y >= 0 && y < m && g[x][y] == 0 && d[x][y] == -1){
// 记录距离
d[x][y] = d[t.first][t.second] + 1;
// 加入到队列
q[ ++ tt ] = {x, y};
}
}
}
// 返回最后一个点距离原点的最短距离
return d[n - 1][m - 1];
}
int main()
{
// 读入 n 和 m
scanf("%d %d", &n, &m);
// d[][] 都初始化为 -1, 表示没有走过
memset(d, -1, sizeof d);
// 读入 n * m 的二维整数数组
for(int i = 0; i < n; i ++ )
for(int j = 0; j < m; j ++ )
scanf("%d", &g[i][j]);
// 输出离终点的最短距离
printf("%d", bfs());
return 0;
}三、树&图的存储
树是一种特殊的图(有向无环图), 与图的存储方式相同
对于无向图中的边
ab, 可以当成存储两条有向边a->b,b->a因此我们可以只考虑有向图的存储。
3.1 邻接矩阵
...
// 稠密图 -> 邻接矩阵
int g[N][N];
...
int main()
{
...
// 初始化邻接矩阵
memset(g, 0x3f, sizeof g);
...
// 读入 m 条边
while( m -- ){
int a, b, c;
scanf("%d %d %d", &a, &b, &c);
// 有重边的情况下取最短的
g[a][b] = min(g[a][b], c);
}
}3.2 邻接表
3.3 链式前向星
// h[] 每个点的出边(数组实现的领接表) w[] 边权重
// e[] 某个编号的点的值; ne[] 某个编号的点的 next; idx 下一次要操作的下标(编号)
int h[N], w[N], e[N], ne[N], idx;
// 增加一条有向边 a->b 权重 c
void add(int a, int b, int c){
e[idx] = b, w[idx] = c, ne[idx] = h[a], h[a] = idx ++;
}
int main()
{
// 初始化邻接表
memset(h, -1, sizeof h);
...
// m 条边
while( m -- ){
int a, b, c;
scanf("%d %d %d", &a, &b, &c);
// 增加一条有向边 a->b 权重 c
add(a, b, c);
}
...
}四、树&图的遍历
4.1 深度优先遍历
模板题:846. 树的重心
示例代码:
#include <cstring>
#include <iostream>
#include <algorithm>
using namespace std;
int n;
const int N = 1e5 + 10, M = N * 2;
// 使用邻接表来存储 树/图 都会有下面这一行
int h[N], e[M], ne[M], idx;
bool st[N]; // 状态数组,dfs中表示某个点搜过了
// 求的是删除某个点后剩余的连通块点数最大值中的最小值
// 所以初始化为最大的,后面用 min 来更新
int ans = N;
// 添加一条有向边 a -> b
void add(int a, int b){
e[idx] = b; // 新节点的值是 b
ne[idx] = h[a]; // 新节点的ne指向首元节点
h[a] = idx ++ ; // 改变头节点的指向并 idx ++
}
// return: 返回以u为根的子树节点数
int dfs(int u){
st[u] = true; // 标记这个点已经搜过
// sum 是以u为根的子树节点数,包含u自己,所以初始化为1
// res 是删掉u后剩下的连通块中节点的最大值,所以初始化小值,后面max更新
int sum = 1, res = 0;
// 遍历节点 u 连通的点
for(int i = h[u]; i != -1; i = ne[i]){
// j 记录遍历到的节点值
int j = e[i];
if(!st[j]){
// 如果没有搜过这个点,那么深搜它
int s = dfs(j);
// 深搜这个点会返回以 j 为根的子树节点数 s
res = max(res, s); // s 是 u 的连通块之一,用于更新一次
sum += s; // 同时 s 是 u 的子树,sum 加上 s
}
}
// 使用 u 上面的一大块来更新 res
res = max(res, n - sum);
// 更新 ans
ans = min(ans, res);
// 返回 sum
return sum;
}
int main()
{
// 初始化用来存储的邻接表: 所有的头节点都指向 -1
memset(h, -1, sizeof h);
cin >> n;
for(int i = 0; i < n - 1; i ++ ){
int a , b;
cin >> a >> b;
// a 和 b 之间存在一条无向边
add(a, b);
add(b, a);
}
// 从一号点开始深搜
dfs(1);
cout << ans << endl;
return 0;
}4.2 广度优先遍历
模板题:847. 图中点的层次
示例代码:
#include <cstring>
#include <iostream>
#include <algorithm>
using namespace std;
int n , m;
const int N = 1e5 + 10;
// 邻接表存储图
int h[N], e[N], ne[N], idx;
// d: 最短距离; q : 队列做 bfs
int d[N], q[N];
// 增加一条由 a -> b 的有向边
void add(int a, int b){
e[idx] = b;
ne[idx] = h[a];
h[a] = idx ++;
}
int bfs(){
// 初始化队列是有一个值的,就是起点,所以 hh == tt
int hh = 0, tt = 0;
// 1号点为起点加入队列
q[0] = 1;
// 初始化 d[]
memset(d, -1, sizeof d);
d[1] = 0; // 一号点距离为 0
while(hh <= tt){
// 队列不空就执行循环
// 取队头
int t = q[ hh ++ ];
// 扩展队头
for(int i = h[t]; i != -1; i = ne[i]){
int j = e[i];
// 如果这个点没更新过
if(d[j] == -1){
d[j] = d[t] + 1;
// 加入队列
q[ ++ tt ] = j;
}
}
}
return d[n];
}
int main()
{
// n 个点, m 条边的有向图
cin >> n >> m;
// 初始化邻接表的静态链表头
memset(h, -1, sizeof h);
while( m -- ){
int a, b;
cin >> a >> b;
add(a, b);
}
cout << bfs() << endl;
return 0;
}五、拓扑排序
拓扑排序(
Topological Sort)是有向无环图(DAG)的一种线性排序方式。它把图中所有顶点排成一个线性序列,使得对于任意一条有向边
u → v,u在序列中都出现在v的前面 。换句话说:如果我们按拓扑序排好,那么有向边的指向始终是从前指向后的
(思考一下应用场景):
排序后的序列保留了 “依赖关系” ——如果 A 依赖 B,那么 B 一定排在 A 前面。
实际中:学生培养计划的安排,例如学习数据结构与算法这门课之前必须先修完程序设计
解题:卡恩(
kahn)算法 -- (BFS 入度表法)- 1). 统计各个节点的入度
- 2). 删除入度为 0 的节点和其与其他点的边
- 3). 重复步骤 2 , 直到图中所有点都被处理或者一直有未处理且入度不为 0 的点(说明图有环)
- 模板题:848. 有向图的拓扑序列
- 示例代码:
#include <iostream>
#include <cstring>
using namespace std;
const int N = 1e5 + 10;
int n, m; // n 个点 m 条 边
// 使用邻接表来存储
int h[N], e[N], ne[N], idx;
// q 是用于 dfs 的队列,d 是存储每个点的入度
int q[N], d[N];
// 增加一条由 a -> b 的有向边
void add(int a, int b){
e[idx] = b, ne[idx] = h[a], h[a] = idx ++;
}
bool topsort(){
int hh = 0, tt = -1;
// 添加所有入度为 0 的点
for(int i = 1; i <= n; i ++ )
if(!d[i])
q[ ++ tt ] = i;
// 下面是 bfs 过程
while(hh <= tt){
// 当队列不空就一直循环
// 取队头
int t = q[ hh ++ ];
// 拓展队头
for(int i = h[t]; i != -1; i = ne[i]){
int j = e[i];
// t 已经入队,删除 t -> j 的这条边,那么j的入度减一
// 如果说减一后为 0, 那么添加进队列
if(-- d[j] == 0)
q[ ++ tt ] = j;
}
}
// 正常情况下:n 个 点按照拓扑序进入队列,那么最后下标是 n - 1
return tt == n - 1;
}
int main()
{
cin >> n >> m;
// 初始化链表头
memset(h, -1, sizeof h);
// 输入 m 条边
while( m -- ){
int x, y;
cin >> x >> y;
add(x, y);
// 增加一条 x -> y 的边记得y入度加一
d[y] += 1;
}
if(topsort()){
// 如果有拓扑序的话,队列的顺序就是拓扑序
for(int i = 0; i < n; i ++ )
cout << q[i] << ' ';
cout << endl;
}else{
cout << "-1" << endl;
}
return 0;
}六、最短路问题
6.1 概览
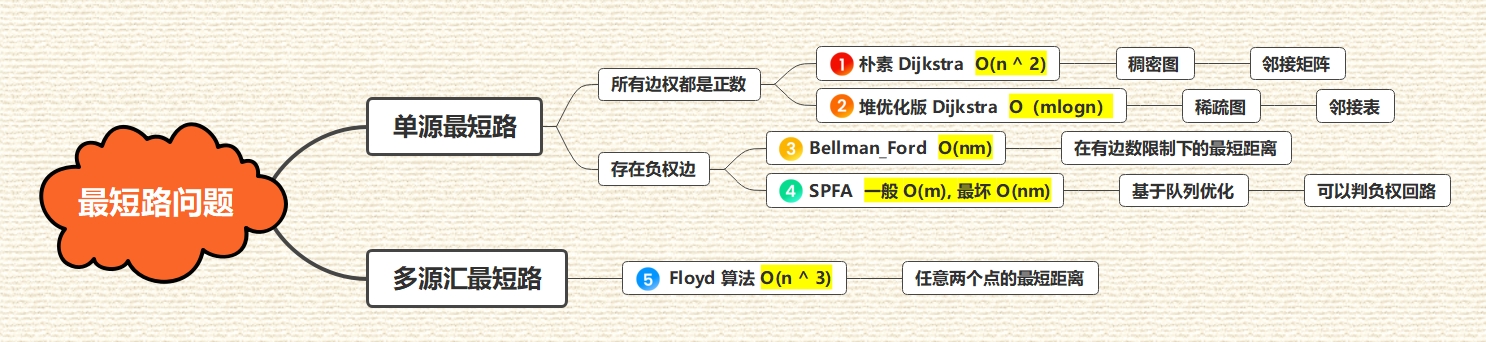
6.2 朴素 Dijkstra
- 作用:在 非负权有向图或无向图 中,求从 单一源点 到 所有其他顶点 的 最短路径(SSSP)。
- 核心思想:
贪心 + 松弛 (relaxation)——每次都把 “当前已知最短路径” 最小的顶点拿出来,用它更新邻居。
示例代码:
#include <iostream>
#include <cstring>
using namespace std;
const int N = 510; // 点的个数 n 最多 500
int n, m; // n 个点 , m 条边
// 朴素 dijkstra 适用于稠密图的情况 --> 稠密图适合使用邻接矩阵来存储
int g[N][N]; // N * N 的 邻接矩阵
int dist[N]; // 存储每个点距离原点的最短距离
bool st[N]; // 存储每个点是否已经被确定最短了
int dijkstra(){
// 初始化 dist[] , 离原点的距离都为无穷大
memset(dist, 0x3f, sizeof dist);
// 初始化原点(1号点)距离原点的dist为0
dist[1] = 0;
// 由于每次是选择一个未确定且最近的点作为中介点来进行一次松弛操作
// 那么总共是 1 ~ n 有 n 个点,取前面 n - 1 个点都做一次松弛操作
// 第 n 个点已经受到了除它外所有点的影响,所以循环只需要 n - 1 次即可
for(int i = 0; i < n - 1; i ++ ){
// 1. 找到目前还没确定的点中距离最近的那个点为 t
int t = -1;
for(int j = 1; j <= n; j ++ ){
if(!st[j] && (t == -1 || dist[t] > dist[j]))
t = j;
}
// 第一步的循环出来之后,目前最近的点为 t
// 2. 使用 t 为中介点,更新所有点的距离
for(int j = 1; j <= n; j ++ ){
// j 距离原点的新距离 = min(j 目前距离原点的距离, t 距离原点的距离 + t -> j 距离)
dist[j] = min(dist[j], dist[t] + g[t][j]);
}
// 把 t 这个点标记为已经是最短距离了
st[t] = true;
}
// 路径不存在输出 -1
if(dist[n] == 0x3f3f3f3f) return -1;
return dist[n];
}
int main()
{
// n 个点,m 条边
scanf("%d %d", &n, &m);
// 初始化邻接矩阵为无穷大: 表示两个点不可达(距离无穷大)
memset(g, 0x3f, sizeof g);
while( m -- ){
// m 行 : 存在一条从点 x 到 点 y 的有向边, 边长为 z
int x, y, z;
scanf("%d %d %d", &x, &y, &z);
// 这种更新方式可以有效避免重边和自环
g[x][y] = min(g[x][y], z);
}
printf("%d", dijkstra()); // 输出 1 号点到 n 号点的最短距离
return 0;
}6.3 堆优化版 Dijkstra
示例代码:
#include <iostream>
#include <algorithm>
#include <cstring>
#include <queue>
using namespace std;
typedef pair<int,int> PII;
const int N = 1e6 + 10;
int n , m;
// 使用邻接表来存储
int h[N], w[N], e[N], ne[N], idx;
int dist[N];
bool st[N];
// 增加一条带权有向边,a -> b , 权值为 c
void add(int a, int b, int c){
e[idx] = b, w[idx] = c, ne[idx] = h[a], h[a] = idx ++;
}
bool dijkstra(){
// 初始化 dist[]
memset(dist, 0x3f, sizeof dist);
dist[1] = 0; // 一号点距离为 0
// 使用小根堆来对 dijkstra 进行优化
priority_queue<PII, vector<PII>, greater<PII>> heap;
// 其中堆的每个元素结构为 {距离原点的距离, 节点编号}
heap.push({0,1}); // 加入起点
while(heap.size()){
// 取距离最短的 t
auto t = heap.top(); heap.pop();
// ver 节点编号,distance 距离
int ver = t.second, distance = t.first;
// 跳过冗余(后面来的一定不是最短,最短的在前面已经确定了)
if(st[ver]) continue;
st[ver] = true; // 如果是第一次搜到那么标记已经是最短距离
// 根据这个节点编号拓展 t
for(int i = h[ver]; i != -1; i = ne[i]){
int j = e[i]; // 取到的 j 都是 t 指向的节点
if(dist[j] > dist[ver] + w[i]){
dist[j] = dist[ver] + w[i];
// 把 j 加入堆
heap.push({dist[j], j});
}
}
}
if(dist[n] > 0x3f3f3f3f / 2) return false;
return true;
}
int main()
{
cin >> n >> m;
// 初始化邻接表表头
memset(h, -1, sizeof h);
while( m -- ){
int x, y, z;
cin >> x >> y >> z;
add(x, y, z);
}
if(dijkstra()){
cout << dist[n] << endl;
}else{
cout << "-1" << endl;
}
return 0;
}6.4 Bellmen_ford
- 模版题:853. 有边数限制的最短路
- 示例代码:
#include <iostream>
#include <cstring>
#include <algorithm>
using namespace std;
// 点最多是 500, 边最多是 10000
const int N = 510, M = 10010;
int dist[N], backup[N];
int n, m, k;
struct edge{
int a,b,c;
}edges[M];
void bellman_ford(){
// 初始化 dist
memset(dist, 0x3f, sizeof dist);
dist[1] = 0; // 1 号点距离为 0
// 最多经过 k 条边的最短距离: 最多可以松弛 k 次 -> k 次迭代
// 补: 一次松弛可以确定与原点有一条边的点的最短距离 (k 次松弛可以确定有 k 条边的最短距离)
for(int i = 0; i < k; i ++ ){
// 每次迭代都要备份一下,使用备份来更新,避免 "串联"
memcpy(backup, dist, sizeof dist);
// 一次松弛操作
for(int j = 1; j <= m; j ++){
int a = edges[j].a, b = edges[j].b, c = edges[j].c;
dist[b] = min(dist[b], backup[a] + c);
}
}
}
int main()
{
// n 个点,m 条边,最多经过 k 条边的约束
cin >> n >> m >> k;
for(int i = 1; i <= m; i ++ ){
// m 行: 点 x 到 点 y 的有向边,边长为 z
int a,b,c;
cin >> a >> b >> c;
edges[i] = {a, b, c};
}
bellman_ford();
if(dist[n] > 0x3f3f3f3f / 2) cout << "impossible" << endl;
else cout << dist[n] << endl;
return 0;
}6.5 SPFA 最短路
- 模版题:851. spfa求最短路
- 示例代码:
#include <iostream>
#include <cstring>
#include <algorithm>
#include <queue>
using namespace std;
// n 个点 m 条边的有向图
int n, m;
// 点和边最大都是 1e5
const int N = 1e5 + 10;
// 使用邻接表来存储
int h[N], w[N], e[N], ne[N], idx;
int dist[N]; // 记录每个点最短距离
bool st[N]; // 当前已经在队列的就不再进队列
// 增加一条 a -> b 的有向边,边长为 c
void add(int a, int b, int c){
e[idx] = b; w[idx] = c; ne[idx] = h[a]; h[a] = idx ++;
}
void spfa(){
// 初始化dist[]
memset(dist, 0x3f, sizeof dist);
dist[1] = 0; // 一号点就是起点,距离为 0
queue<int> q;
q.push(1); // 一号点加入队列
st[1] = true; // 标记一号点已经在队列
while(q.size()){
// 当队列不空
// 取队头
int t = q.front(); q.pop();
// 标记一号点出了队列
st[t] = false;
// 扩展队头(使用 t 做一轮松弛操作)
for(int i = h[t]; i != -1; i = ne[i]){
int j = e[i]; // j 为每个 t 指向的节点
if(dist[j] > dist[t] + w[i]){
dist[j] = dist[t] + w[i];
// j 的值发生了改变(肯定是变小了), 那么它的出边可以再次更新
// 如果 j 不在队列 把 j 加入队列,并标记
if(!st[j]){
q.push(j);
st[j] = true;
}
}
}
}
}
int main()
{
cin >> n >> m;
// 初始化链表头
memset(h, -1, sizeof h);
while( m -- ){
// m 行: x -> y 边长为 z,z 可能为负数
int x, y, z;
cin >> x >> y >> z;
add(x, y, z);
}
// 调用 spfa
spfa();
// 因为每条边都是又起点拓展过去的,如果没更新那么就直接跟节点没有连通,只能是 0x3f3f3f3f
if(dist[n] == 0x3f3f3f3f) cout << "impossible" << endl;
else cout << dist[n] << endl;
return 0;
}6.6 SPFA 判断负环
模板题:852. spfa判断负环
示例代码:
#include <iostream>
#include <cstring>
#include <algorithm>
#include <queue>
using namespace std;
// 点最大为 2000, 边最大为 1e4
const int N = 2010, M = 1e4 + 10;
int n, m;
// 使用邻接表来存储
int h[N], e[M], w[M], ne[M], idx;
int dist[N]; // 每个点最短距离
int st[N]; // 某个点是否此时在队列中
int cnt[N];
// 增加一个有向边 a->b, 边长为 z,z 可能为负数
void add(int a, int b, int c){
e[idx] = b; w[idx] = c; ne[idx] = h[a]; h[a] = idx ++;
}
// 返回一个布尔值表示图中是否存在负环回路
bool spfa(){
queue<int> q;
// 与求最短路不同的是: 这里不能只把起点加入到队列
// 因为有些地方起点可能不可达,那么就无法找到负权回路
// 所以一开始要把所有点都加入到队列里面
for(int i = 1; i <= n; i ++ ){
st[i] = true;
q.push(i);
}
while(q.size()){
// 这里不需要初始dist
// 有负权回路的话,dist 里的值会向负无穷不断逼近;
// 没负权回路的话,dist 向负值方向变化的趋势会在某一个时候停止。
// 只要 dist 的值在减小,就记录进队,继续用于更新
// 停止的关键在 cnt >= n
// 当队列不空
// 取队头
int t = q.front(); q.pop(); st[t] = false;
// 拓展队头
for(int i = h[t]; i != -1; i = ne[i]){
int j = e[i];
if(dist[j] > dist[t] + w[i]){
dist[j] = dist[t] + w[i];
cnt[j] = cnt[t] + 1;
// 如果某个点的边数大于等于 n 了,说明点的数量大于等于 n+1
// 而我们一共点最多就 n 个, 由抽屉原理可知:一定至少有两个点是一样的
// 说明有环,那么又因为我们spfa只有距离短才更新,所以这个回路一定是负权回路
if(cnt[j] >= n) return true;
if(!st[j]){
q.push(j);
st[j] = true;
}
}
}
}
return false;
}
int main()
{
scanf("%d %d", &n, &m);
// 初始化链表头
memset(h, -1, sizeof h);
while( m -- ){
int x, y, z;
scanf("%d %d %d", &x, &y, &z);
add(x, y, z);
}
if(spfa()) cout << "Yes" << endl;
else cout << "No" << endl;
return 0;
}6.7 Floyd
- 与之前都不同的是 :
Floyd可以求任意两个点的最短距离,当然时间复杂度也高O(n ^ 3) - 思想:基于
动态规划 + 松弛 (relaxation)- “ 按节点编号从小到大逐个 ’ 放行 ‘,只允许用前
k个节点做中转,去更新所有点对的最短路。”
- “ 按节点编号从小到大逐个 ’ 放行 ‘,只允许用前
模板题:854. Floyd求最短路
示例代码:
#include <iostream>
#include <cstring>
#include <algorithm>
using namespace std;
const int N = 210, INF = 1e9;
// n 个点 m 条边 Q 个 询问
int n, m, Q;
int d[N][N]; // 邻接矩阵(任意两条边的距离)
void floyd(){
for(int k = 1; k <= n; k ++ ){
for(int i = 1; i <= n; i ++ ){
for(int j = 1; j <= n; j ++ ){
d[i][j] = min(d[i][j], d[i][k] + d[k][j]);
}
}
}
}
int main()
{
cin >> n >> m >> Q;
// 初始化d[]
for(int i = 1; i <= n; i ++ ){
for(int j = 1; j <= n; j ++ ){
if(i == j) d[i][j] = 0;
else d[i][j] = INF;
}
}
// 读入 m 行 x-> y 一条有向边,边长为 z
while( m -- ){
int x, y, z;
cin >> x >> y >> z;
// 避免重边,自环的更新
d[x][y] = min(d[x][y], z);
}
floyd();
// 处理询问
while( Q -- ){
int x , y;
cin >> x >> y;
if(d[x][y] > INF / 2) cout << "impossible" << endl;
else cout << d[x][y] << endl;
}
return 0;
}七、最小生成树
7.1 概览
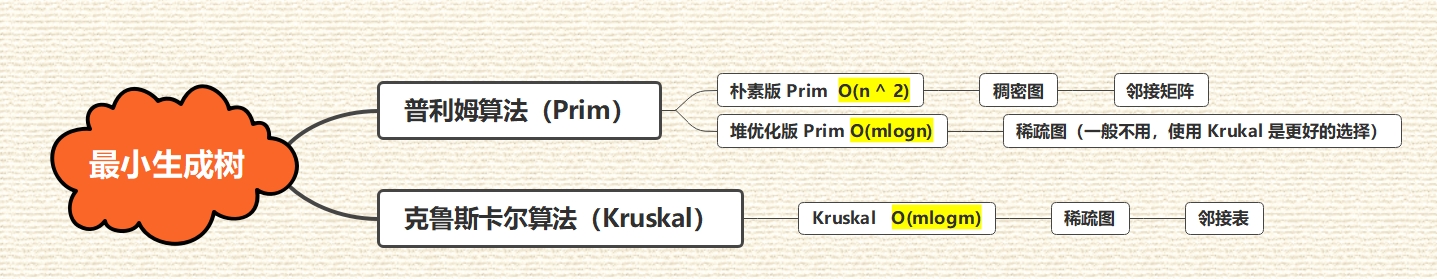
7.2 Prim
- 模板题:858. Prim算法求最小生成树
- 示例代码:
#include <iostream>
#include <cstring>
#include <algorithm>
using namespace std;
// n 个点 m 条边的无向图
int n, m;
const int N = 510, INF = 0x3f3f3f3f;
int g[N][N]; // 邻接矩阵
int dist[N]; // 注意这里没有原点了,这里表示点和集合的距离
bool st[N]; // 某个点是否进入集合
int prim(){
// 初始化 dist
memset(dist, 0x3f, sizeof dist);
int res = 0; // 最小生成树的树边权重之和
for(int i = 0; i < n; i ++ ){ // n 个点,所以 n 次迭代
int t = -1; // -1 表示还没选, t 最后选中还没选中且集合最近的点,用它松弛出边,且进入集合
for(int j = 1; j <= n; j ++){
if(!st[j] && (t == -1 || dist[t] > dist[j]))
t = j;
}
// 如果不是第一个点,且这个点离集合无穷大,说明图不连通
if(i && dist[t] == INF) return INF;
// 如果不是第一个点, 那么这个距离加入res
if(i) res += dist[t];
// 标记已经确定为集合中的
st[t] = true;
// 使用 t 去松弛出边
for(int j = 1; j <= n; j ++ )
dist[j] = min(dist[j], g[t][j]);
}
return res;
}
int main()
{
cin >> n >> m;
// 初始化 g
memset(g, 0x3f, sizeof g);
while( m -- ){
// m 行 点 u 到 点 v 之间存在一条权值为 w 的无向边
int u, v, w;
cin >> u >> v >> w;
// 注意点1: 因为是无向边,要双向赋值
// 注意点2: 使用 min ,避免重边
g[u][v] = g[v][u] = min(g[u][v], w);
}
int t = prim();
if( t == INF) cout << "impossible" << endl;
else cout << t << endl;
return 0;
}7.3 Kruskal
示例代码:
#include <iostream>
#include <algorithm>
using namespace std;
const int N = 1e5 + 10, M = 2e5 + 10, INF = 0x3f3f3f3f;
int n, m;
int p[N]; // 并查集的祖宗节点
struct Edge{
int a, b, w;
// 重载小于号(比较两个edge是比较两个边的权重)
bool operator< (const Edge &W) const{
return w < W.w;
}
}edges[M];
// 返回节点 u 的祖宗节点 + 路径压缩
int find(int u){
if(p[u] != u) p[u] = find(p[u]);
return p[u];
}
int kruskal(){
// 先把边按边的权重进行排序
sort(edges, edges + m);
//初始化并查集(都指向自己)
for(int i = 1; i <= n; i ++ ) p[i] = i;
int res = 0, cnt = 0;
// 因为已经排序,这是从小到大遍历出所有的边
for(int i = 0; i < m; i ++ ){
int a = edges[i].a, b = edges[i].b, c = edges[i].w;
// 如果 a 和 b 不连通
a = find(a); b = find(b);
if(a != b){
// 先连通两个边
p[a] = b;
// 记录 res
res += c;
// 最小生成树边数 cnt + 1
cnt ++;
}
}
// n 个点 应当有 n - 1 条边,如果小于则不连通
if(cnt < n - 1) return INF;
return res;
}
int main()
{
cin >> n >> m;
for(int i = 0; i < m; i ++ ){
int u, v, w;
cin >> u >> v >> w;
edges[i] = {u, v, w};
}
int t = kruskal();
if(t == INF) cout << "impossible" << endl;
else cout << t << endl;
return 0;
}